
Certificate Course in
Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare
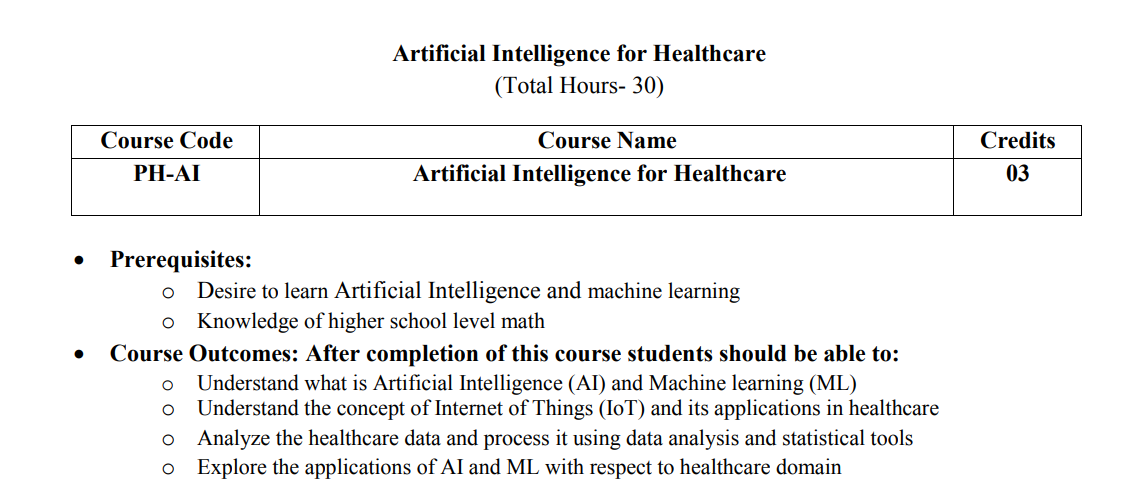
Syllabus Link: AI for Healthcare Syllabus
- Teacher: Admin User

Certificate Course in
Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare

Syllabus Link: AI for Healthcare Syllabus
Data Science Using Python Submission course is a course for performing submission of ITL604 Lab for AY 2022-23 Batch of IT Department.


Mini Project – 1 A for Front end/back end Application using JAVA

Computer programming Paradigms Lab

SQL Lab
Lab Objectives:
The Lab experiments aims:
Data Structures Lab
Lab Objectives:
The Lab experiments aims:

Paradigms and Computer Programming Fundamentals
Course Objectives:
The course aims:

Principle of Communication
Course Objectives:
The course aims: